In a world where everything from coffee makers to heavy machinery is getting smarter, industrial IoT (IIoT) is the unsung hero behind the scenes. Imagine a factory floor where machines chat like old friends, sharing data faster than you can say “efficiency.” It’s not just a tech trend; it’s a revolution that’s transforming how industries operate, boosting productivity while keeping costs in check.
But wait—before you roll your eyes at yet another tech buzzword, consider this: IIoT isn’t just for tech geeks in lab coats. It’s for anyone who wants to make their operations smoother and their bottom line fatter (and who doesn’t?). So, buckle up as we dive into the fascinating world of IIoT, where innovation meets practicality, and discover why it’s time to embrace this game-changing technology.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Industrial IoT (IIoT) refers to the network of connected devices within industrial settings. This technology enables machines and systems to communicate seamlessly, transforming workflows and enhancing data collection. Organizations leverage data from sensors and devices to gain insights that drive operational efficiency.
In IIoT environments, real-time monitoring plays a crucial role. Sensors collect data from equipment, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime. Predictive analytics helps in identifying potential issues before they escalate, thus protecting investments and resources.
Security remains a critical concern in IIoT implementations. Safeguarding data and connectivity from cyber threats is essential for successful deployment. Employing robust security measures mitigates risks associated with connected devices and industrial networks.
Moreover, data integration is at the heart of IIoT solutions. Connecting previously isolated systems allows for streamlined operations and improved decision-making. Integration fosters collaboration across departments and enables the analysis of large data sets for actionable insights.
Enhanced automation capabilities result from IIoT adoption. Automated processes reduce human error and improve production speeds, leading to higher output. Furthermore, IIoT facilitates remote monitoring, enabling operators to manage systems from anywhere in the world.
Ultimately, IIoT represents a paradigm shift in industrial operations. It introduces efficiency and agility while reducing costs and waste. Companies that embrace IIoT stand to gain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
Key Components of IIoT
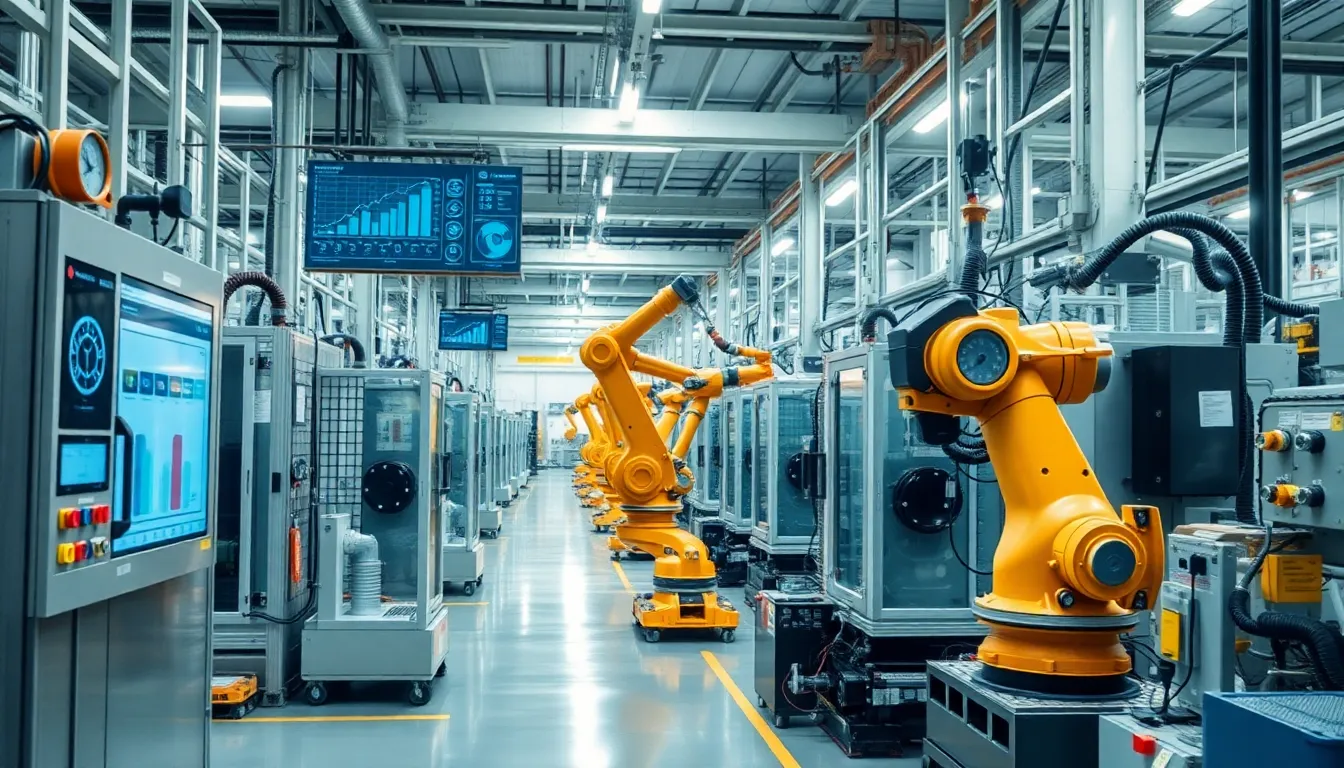

Key components of industrial IoT (IIoT) contribute significantly to its functionality and effectiveness in modern industries. Each element plays a vital role in driving connectivity, data analysis, and operational efficiency.
Sensors and Actuators
Sensors capture critical data from machines and processes, enabling accurate real-time monitoring. Types of sensors include temperature, pressure, and vibration sensors, each serving specific purposes in various industrial applications. Actuators receive signals from controllers to perform physical actions, such as opening a valve or moving a robotic arm. These devices together enhance system responsiveness and support predictive maintenance by monitoring equipment health continuously.
Connectivity Solutions
Connectivity solutions form the backbone of IIoT by enabling devices to communicate seamlessly. Technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks facilitate data transmission between machines and cloud systems. Edge computing optimizes this communication by processing data closer to its source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. Reliable and secure connectivity ensures uninterrupted operations while enhancing collaboration among different industrial systems.
Data Analytics and Cloud Computing
Data analytics transforms raw data collected from sensors into actionable insights. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns and predict potential issues, allowing for proactive decision-making. Cloud computing provides scalable storage and processing power, enabling easy access to data from anywhere. This integration of analytics and cloud solutions empowers industries to enhance operational efficiency and optimize resource allocation effectively.
Benefits of Implementing IIoT
Implementing industrial IoT (IIoT) delivers numerous advantages across various industrial sectors. Increased automation, real-time data access, and enhanced system integration foster operational improvements.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Operational efficiency rises significantly through IIoT adoption. Sensors collect vital data from machinery, enabling predictive maintenance that minimizes downtime. Streamlined processes allow for better resource allocation, ensuring machinery operates at optimal levels. Machine learning algorithms analyze data patterns, enhancing decision-making. Increased communication between devices promotes real-time adjustments, maximizing throughput. As a result, companies witness shorter production cycles, leading to higher output.
Enhanced Safety and Security
Safety and security standards improve notably with IIoT implementation. Continuous monitoring of equipment allows for immediate identification of anomalies. This proactive approach reduces workplace accidents stemming from equipment failures. IIoT solutions integrate advanced security protocols, safeguarding sensitive data related to operations. Employee safety increases through smart wearables that monitor vital signs and environmental conditions. Enhanced visibility into operations promotes a culture of safety awareness among staff.
Cost Reduction
Cost reduction emerges as a key benefit of IIoT systems. By minimizing equipment failures through proactive maintenance, organizations significantly decrease repair expenses. Optimized resource management leads to lower energy consumption, directly impacting operational costs. Accurate data analytics provides insights that streamline supply chain operations, reducing excess inventory. Businesses experience the advantages of enhanced productivity, ultimately translating into higher profit margins. Overall, IIoT implementations yield substantial cost savings while improving financial performance.
Challenges and Considerations
Industrial IoT (IIoT) presents several challenges that businesses must navigate for successful implementation. Key considerations include data privacy, system integration, and workforce training.
Data Privacy and Security Risks
Data privacy poses significant challenges in IIoT environments. Cybersecurity threats increase as devices and systems connect, heightening vulnerabilities. Protecting sensitive information requires robust encryption methods and ongoing monitoring. Regulations such as GDPR emphasize compliance, obliging organizations to address user data protection diligently. Security protocols must adapt as threats evolve, ensuring strategic defenses minimize risks effectively.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Integrating IIoT with legacy systems can complicate implementations. Many businesses rely on older technologies that may not support new protocols. Compatibility issues arise, potentially hindering data flow and system functionality. Employing middleware solutions enhances communication between legacy systems and modern IoT devices. Furthermore, a phased integration approach can facilitate smoother transitions, allowing for gradual adaptation and minimizing disruptions in operations.
Skill Gaps and Workforce Training
A lack of skilled personnel poses challenges for IIoT adoption. Organizations often face gaps in expertise related to IoT technologies and data analytics. Investing in training programs helps equip employees with necessary skills. Collaborative learning environments foster knowledge sharing across teams, promoting a culture of continuous improvement. Businesses can benefit from strategic partnerships with educational institutions to enhance workforce capabilities.
Future Trends in Industrial IoT (IIoT)
The landscape of Industrial IoT continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for efficiency. Trends emerge that shape the future of IIoT, enhancing productivity and operational capabilities.
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence plays a pivotal role in IIoT, transforming data analysis and decision-making processes. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and optimize operations in real time. Predictive analytics powered by AI increases the accuracy of maintenance schedules, reducing downtime and costs. Enhanced AI tools also facilitate automation, making processes more efficient with less human intervention. Consequently, industries experience improved responsiveness to changes in the market or production needs.
Adoption of Edge Computing
Edge computing significantly enhances IIoT deployment by processing data closer to the source. Devices can analyze information at the edge, reducing latency and improving response times. Real-time insights generated at the edge allow organizations to make swift decisions without relying solely on centralized data centers. This approach also reduces bandwidth costs, as less data needs transmission to the cloud. Enhanced security measures emerge through localized data handling, minimizing vulnerabilities associated with data transmission. As a result, companies experience increased operational efficiency and agility in adapting to market demands.
Industrial IoT is reshaping the landscape of modern industries by driving efficiency and productivity. As companies adopt IIoT technologies they unlock new levels of operational excellence and cost savings. The integration of connected devices and advanced analytics empowers organizations to make informed decisions and respond swiftly to challenges.
While the journey to full IIoT implementation comes with hurdles such as data security and workforce readiness the rewards are undeniable. Embracing IIoT not only enhances operational capabilities but also positions businesses for future growth in an increasingly competitive market. As technology continues to evolve the potential for IIoT to transform industries remains vast and promising.